Truth Tables of Five Common Logical Connectives or Operators ChiliMath
This tool generates truth tables for propositional logic formulas. You can enter logical operators in several different formats. For example, the propositional formula p ∧ q → ¬r could be written as p /\ q -> ~r , as p and q => not r, or as p && q -> !r . The connectives ⊤ and ⊥ can be entered as T and F .
Example 9.6 An implication table example
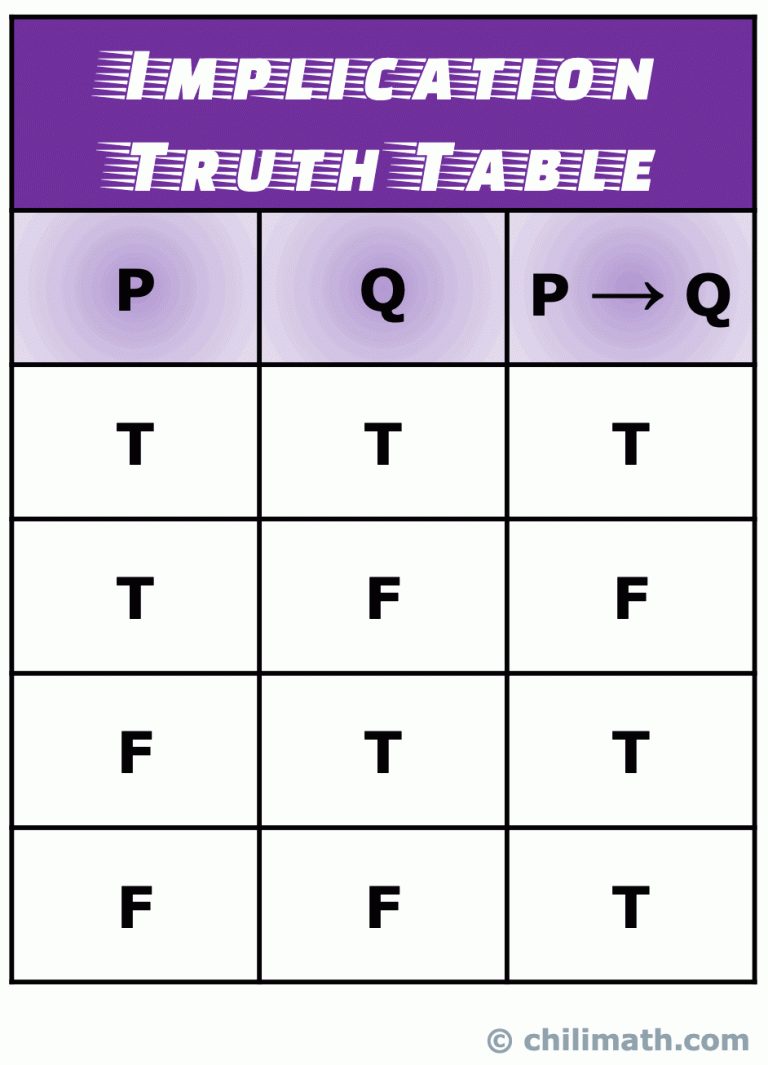
For each truth table below, we have two propositions: p and q. They can either both be true (first row), both be false (last row), or have one true and the other false (middle two rows). Writing this out is the first step of any truth table. The conditional - "p implies q" or "if p, then q"

Implication Truth Table Logical Connectives Stock Vector (Royalty Free
A truth table is one of those things in mathematics that is much easier to understand when you see how it looks and how it works, than learning through its definition. Anyway, we will attempt to define it in order to have a baseline or basic understanding of what it is.. Implication or Conditional. Symbol: [latex]\Rightarrow[/latex] is read.

Implication Truth table discrete mathematics YouTube
Propositional Logic, Truth Tables, and Predicate Logic (Rosen, Sections 1.1, 1.2, 1.3) TOPICS • Propositional Logic • Logical Operations • Equivalences • Predicate Logic .. original implication. Prove it! so now we have: p → q ≡ ¬p ∨ q ≡ ¬q → ¬p . Predicate Logic ! Some statements cannot be expressed in

Logical Implication Truth Table Explained Elcho Table
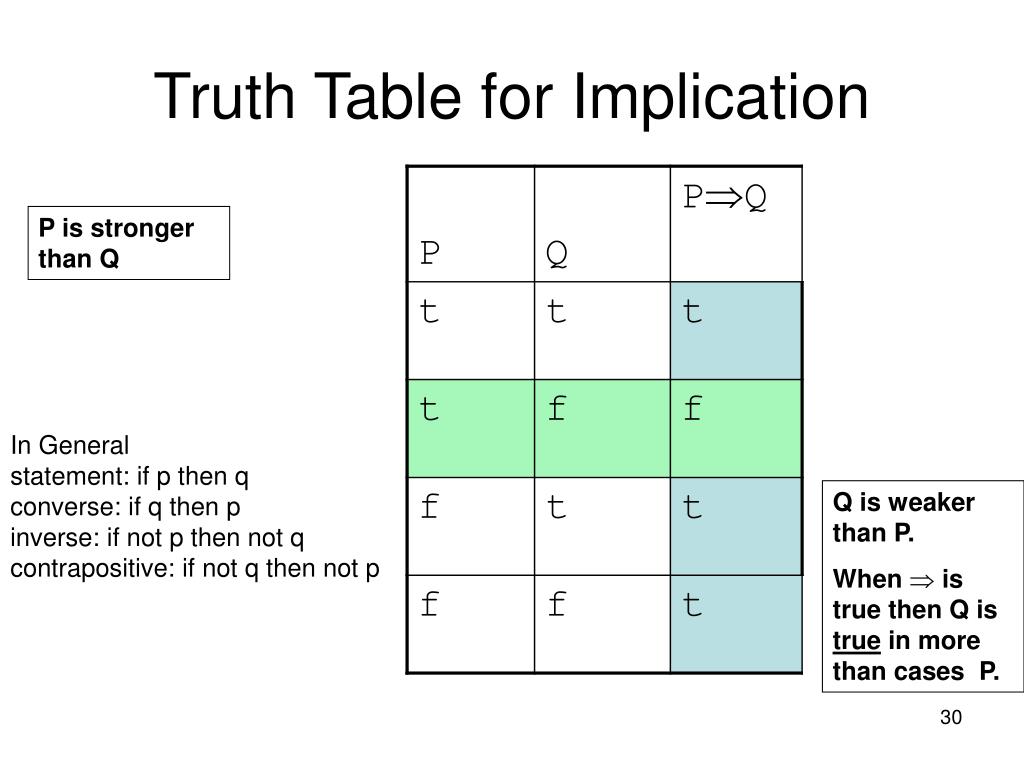
Truth Table for Implication p q p → q F F T T F F T T The implication is only false if p is true and q isn't. It's true otherwise. The implication is only false if p is true and q isn't. It's true otherwise. You will need to commit this table to memory. (Consider a tattoo on your forearm.) We're going to be using it a lot over the.

Implication Truth Table Explained
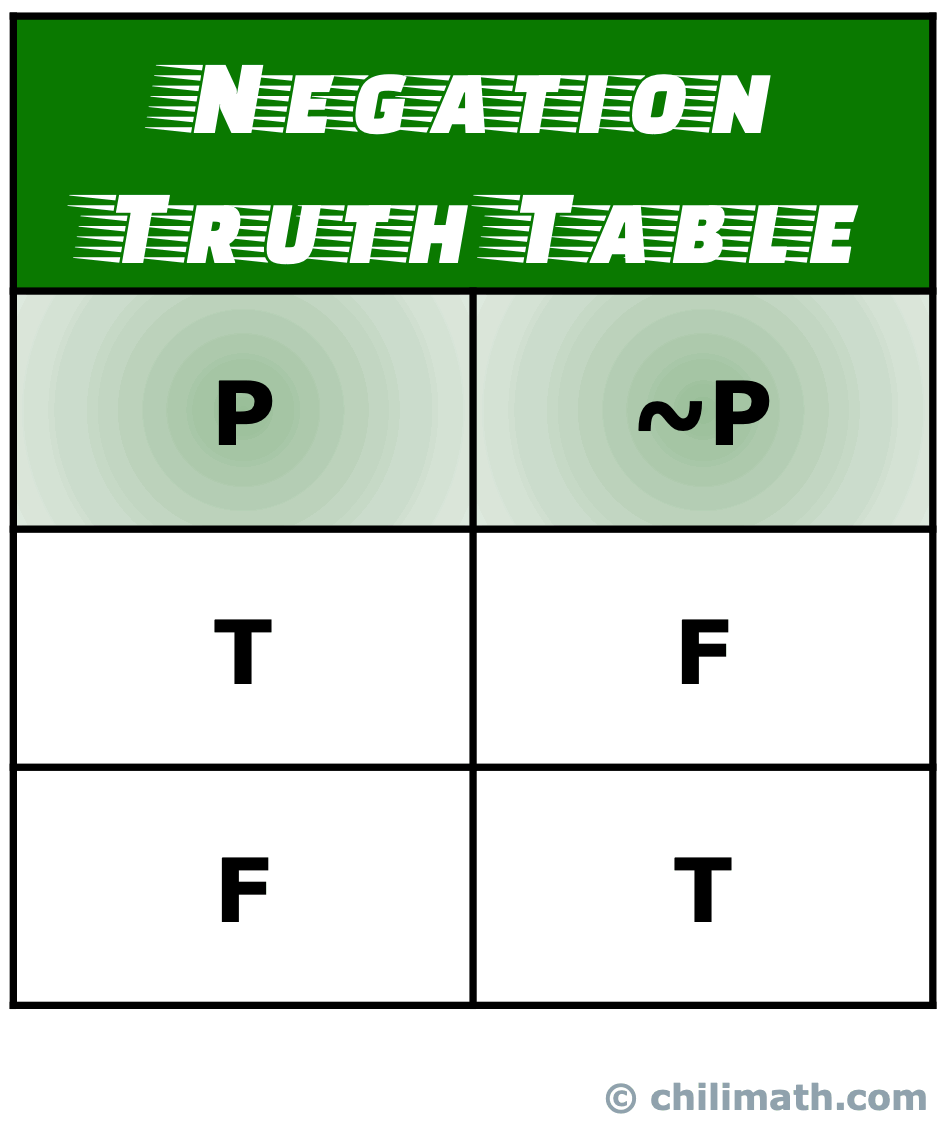
A truth table is a table whose columns are statements, and whose rows are possible scenarios. The table contains every possible scenario and the truth values that would occur. One of the simplest truth tables records the truth values for a statement and its negation. Figure %: The truth table for p, âàüp

Truth Table for an Implication (p V q) implies p YouTube
What this truth table represents is the fact that if you have a data set (or situations) that results in a false value of (~A V B) then your assumption that A implies B is violated (or is not correct). In simpler words, the true values in the truth table are for the statement A implies B.
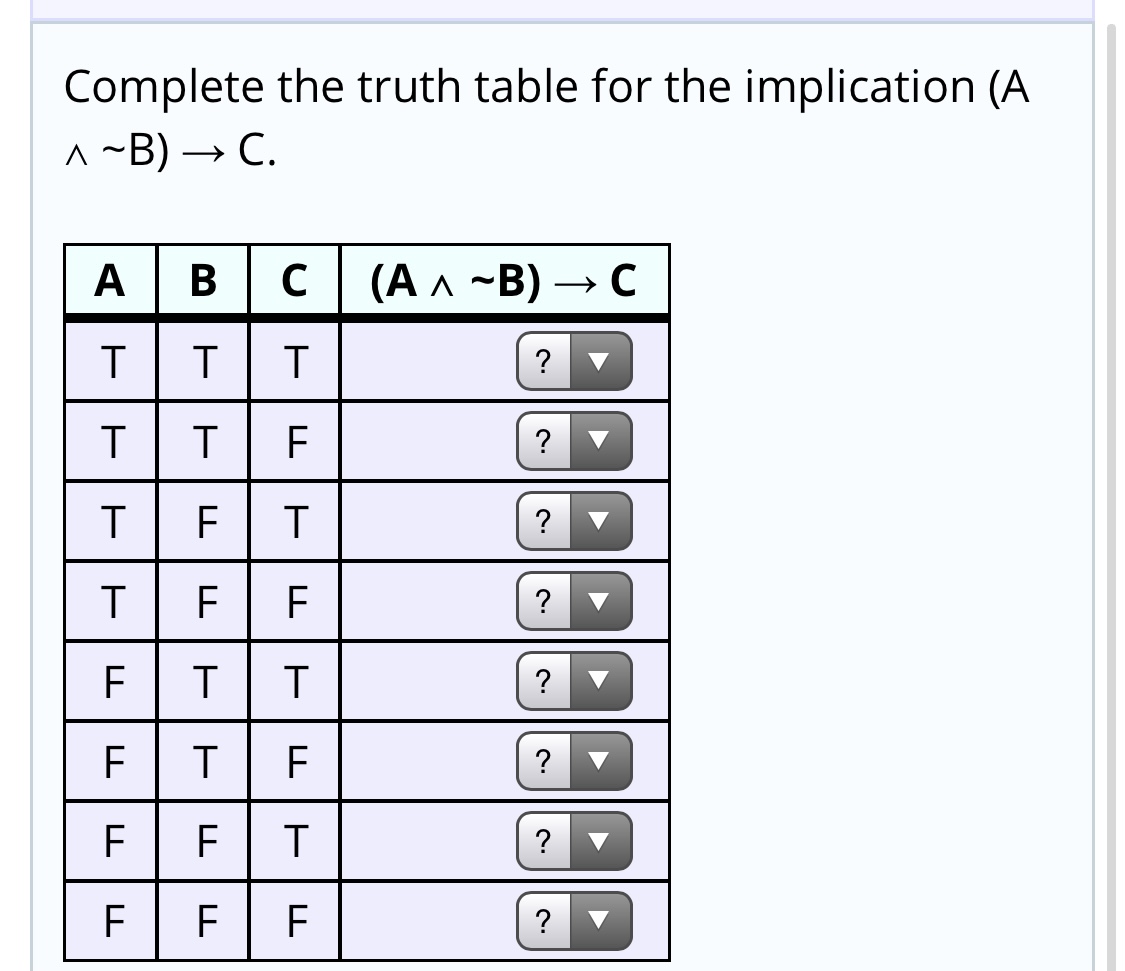
Answered Complete the truth table for the… bartleby
1 The discussion is about why the statement ⊥ → ⊥ ⊥ → ⊥ is considered "true" rather than "false". That is, why the truth table of the conditional connective is defined as it is. An argument is considered valid if, it guarantees the conclusion is true when all the premises are true.

Illustration of “IMPLICATION” logic gate” Truth table corresponding to
A Truth Table is a table that lists all the possible combinations of inputs and their corresponding outputs. It shows how the output of logic circuits changes with different combinations of logic levels at the input. It is mostly associated with Boolean algebra or areas where Boolean logic is used.
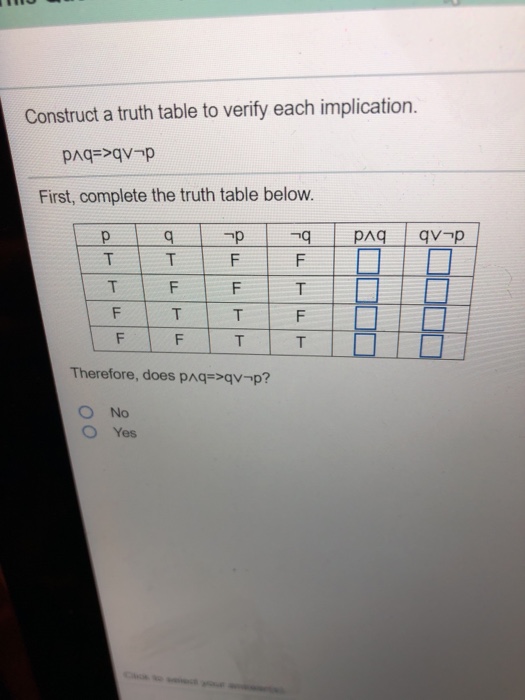
Solved Construct a truth table to verify each implication.
Disjunction (OR) Negation Conditional or Implication Statements A Family of Seven Biconditional Logic Logic Gates Combining Arguments (in progress) See Also Conjunction (AND) Two simple statements can be converted by the word "and" to form a compound statement called the conjunction of the original statements.
Logical Implication Truth Table Explained Elcho Table
Conditional Statement Truth Table Biconditional Statement Now, another necessary type of implication is called a biconditional statement. A biconditional statement, sometimes referred to as a bi-implication, may take one the following forms: P if and only if q P is necessary and sufficient for q If p then q, and conversely
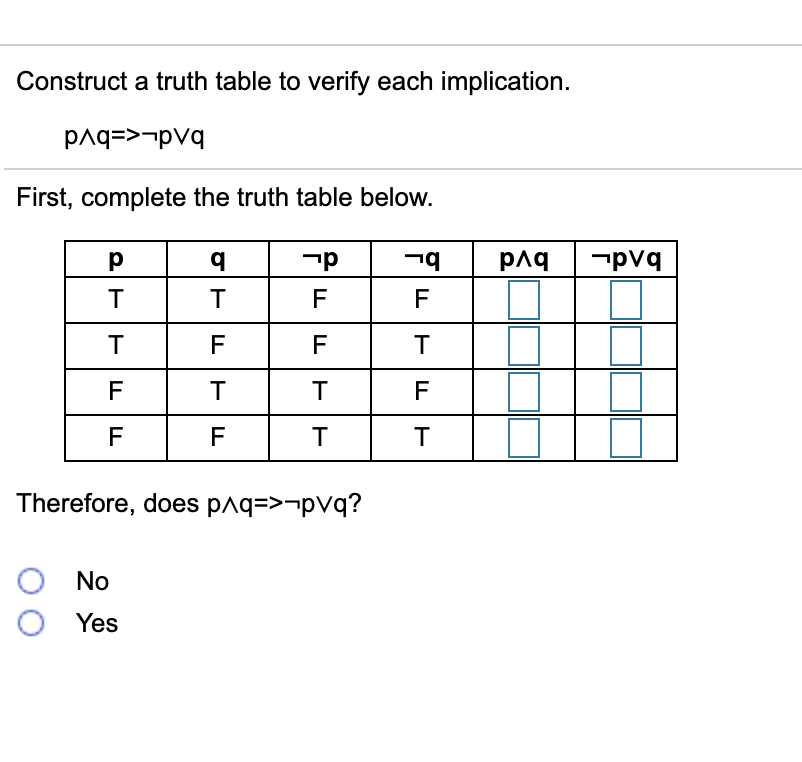
Solved Construct a truth table to verify each implication
Truth Table for Implication p q p → q F F T T F F T T The implication is only false if p is true and q isn't. It's true otherwise. The implication is only false if p is true and q isn't. It's true otherwise. You will need to commit this table to memory. We're going to be using it a lot over the rest of the week. You will need to.

Logical Implication (Fully Explained w/ 15 Examples!)
An implication is an "if-then" statement, where the if part is known as the antecedent, and the then pa. Learn how to create a truth table for an implication.
Logic Example Truth Tables with Biconditionals YouTube
Create a truth table for the statement A ⋀ ~(B ⋁ C) It helps to work from the inside out when creating truth tables, and create tables for intermediate operations. We start by listing all the possible truth value combinations for A, B, and C. Notice how the first column contains 4 Ts followed by 4 Fs, the second column contains 2 Ts, 2 Fs.
PPT Computing Fundamentals 1 Lecture 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free
Use a truth table to interpret complex statements or conditionals. Write truth tables given a logical implication, and its related statements. Determine whether two statements are logically equivalent. Because complex Boolean statements can get tricky to think about, we can create a truth table to break the complex statement into simple.

Truth Table Double Implication YouTube
A truth table is a structured representation that presents all possible combinations of truth values for the input variables of a Boolean function and their corresponding output values. A function f from A to F is a special relation, a subset of A×F, which simply means that f can be listed as a list of input-output pairs.